CADOS: Configurability-Aware Development of Operating Systems (DFG: LO 1719/3-2)
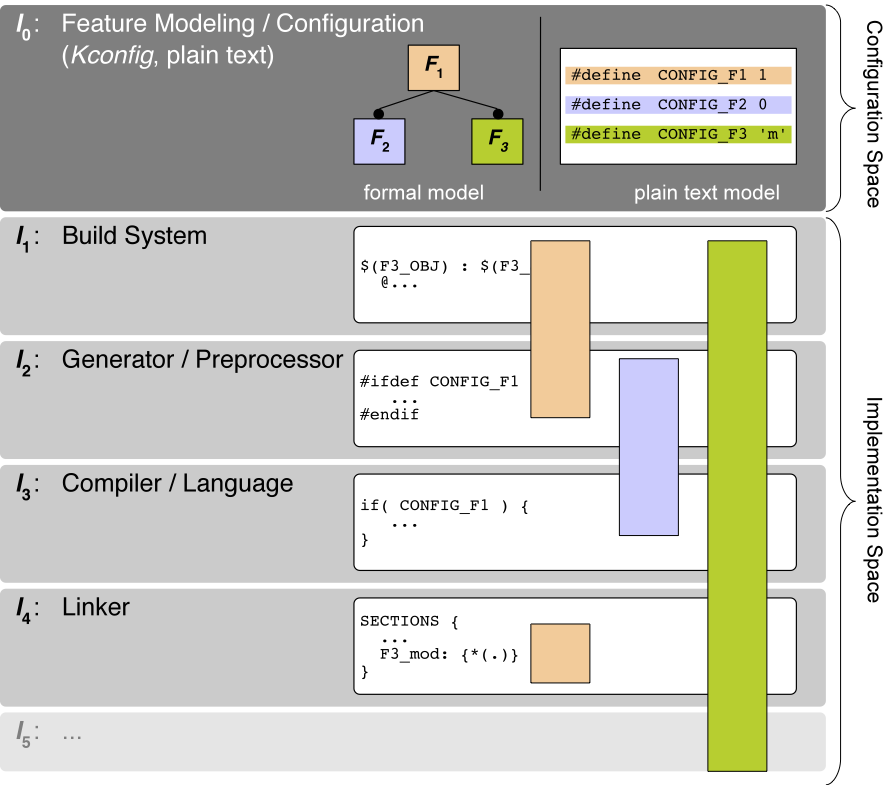
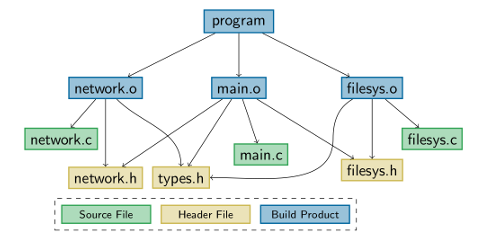
Todays operating systems (as well as other system software) offer a great deal of static configurability to tailor them with respect to a specific application or hardware platform. Linux 4.2, for instance, provides (via its Kconfig models and tools) more than fifteen thousand configurable features for this purpose. Technically, the implementation of all these features is spread over multiple levels of the software generation process, including the configuration system, build system, C preprocessor, compiler, linker, and more. This enormous variability has become unmanageable in practice; in the case of Linux it already has led to thousands of variability defects within the lifetime of Linux. With this term, we denote bugs and other quality issues related to the implementation of variable features. Variability defects manifest as configuration consistency and configuration coverage issues.
In the CADOS project, we investigate scalable methods and tools to grasp the variability on every layer within the configuration and implementation space, visualize and analyze it and, if possible, adjust it while maintaining a holistic view on variability.
Our findings have already led to more than 100 accepted patches in the Linux mainline kernel (see our EuroSys '11 and SPLC '12 papers) and an approach for the automatic tailoring of Linux server systems in order to reduce the exploitable code base (see our HotDep '12 paper). The issue of configuration coverage is addressed in our USENIX '14 paper. Our scalable AST-based hashing method to detect relevant changes in C-source files got a best paper award at USENIX '17. Its extension to extrapolate these changes to changes in run-time behavior of programs (e.g., unit tests) received a best student paper award at ICSOFT '22.
Tools
Various tools assist our analysis of the variability in the Linux kernel and other software projects. Our most important tool is called the undertaker, which searches and reports dead and undead conditional CPP blocks. Since its inception within VAMOS, it has matured to a toolbox of utilities for answering various research questions related to variability in general. For further details, please look into the undertaker trac.
Patch Filtering in Software Product Lines
In the face of critical security vulnerabilities, patch, and update management are a crucial and challenging part of the software life cycle. In statically configured system software, patching becomes even more challenging as we have to support different variants, which are not equally affected by critical patches. While the naive “better-patched-than-sorry” approach will apply all necessary updates, it provokes avoidable costs for developers and customers. Especially, in the embedded domain, where customer-specific variants are prevalent and deployment is expensive, patch management has to become variability-aware. Therefore, we have developed a tool that, given a change, detects which variants are affected by it. This is achieved by storing which parts of a software are used during compilation of all variants. Parts affected by a potential change can then be compared against the used parts of each variant.
TASTING
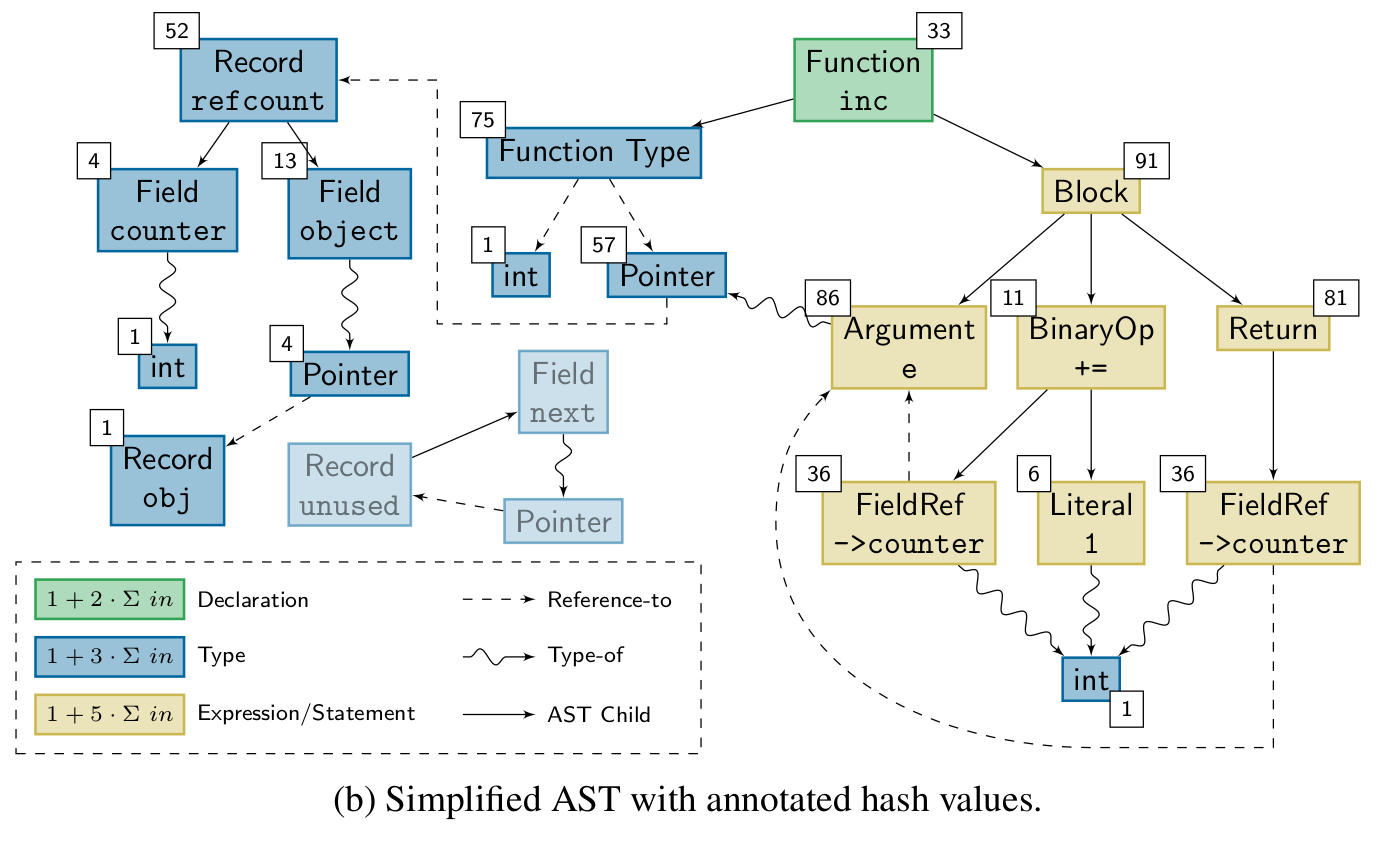
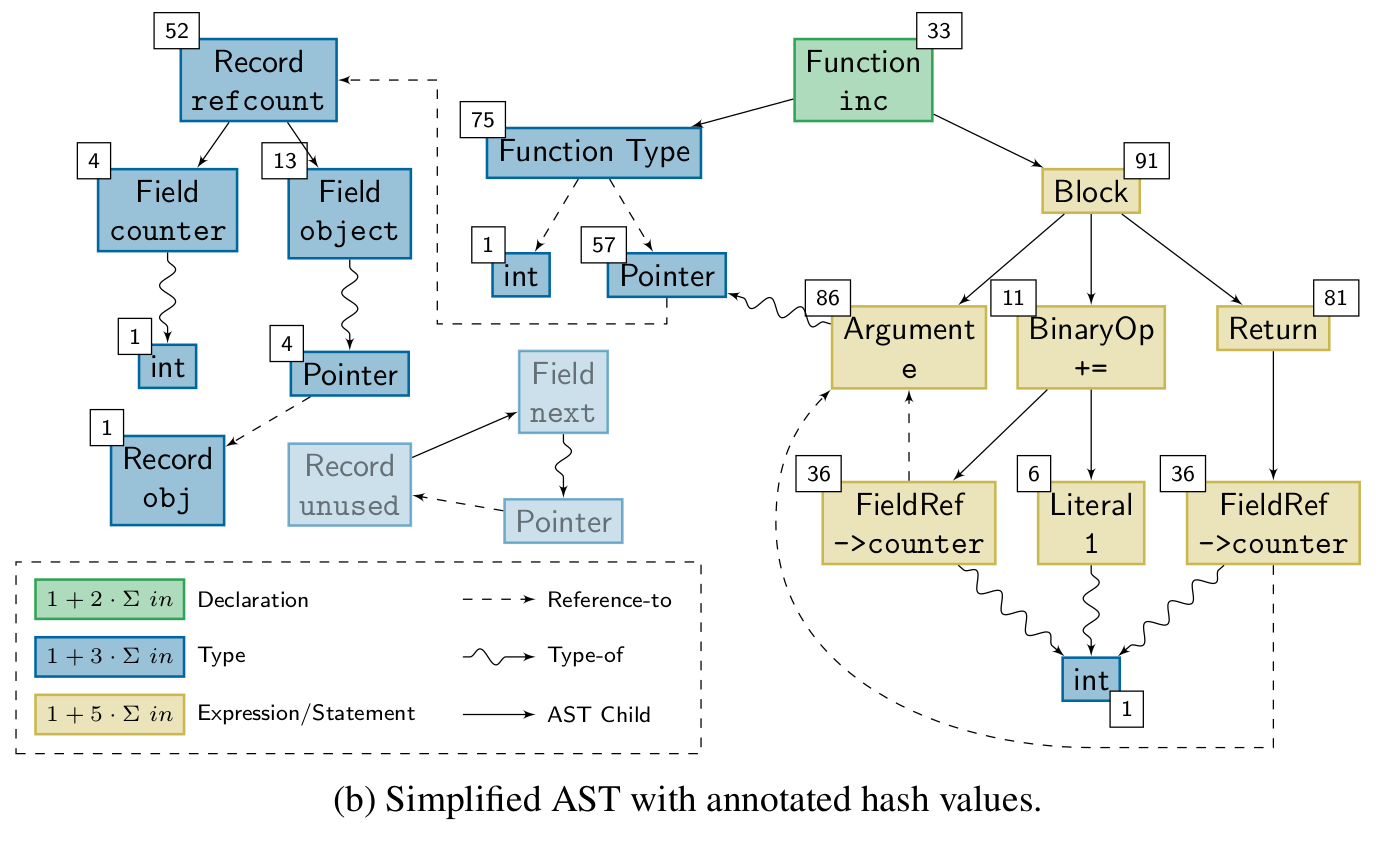
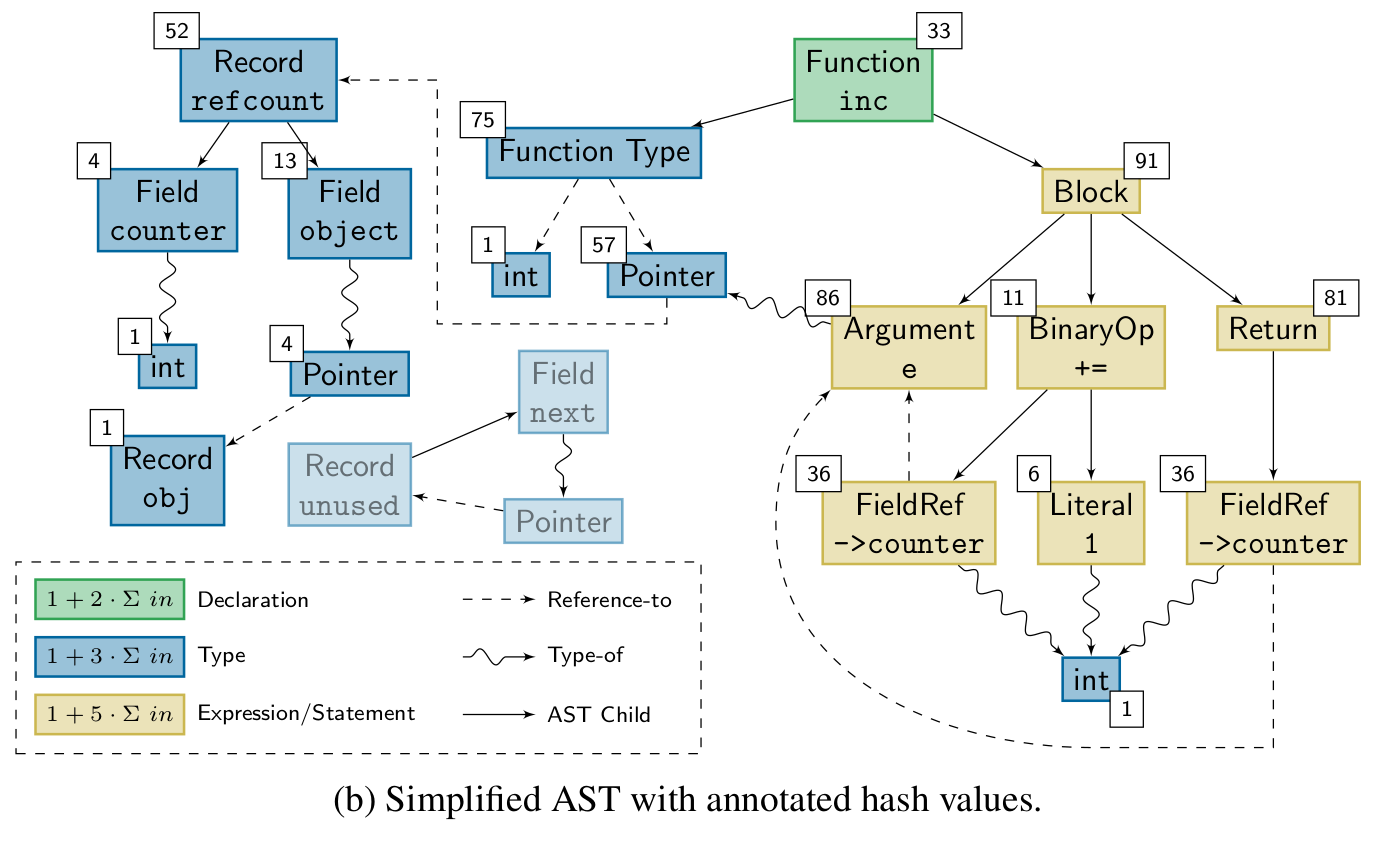
Knowing whether a change affects the run-time behavior of a program can be valuable information. TASTING provides this information by building on top of cHash. Combining the ASTs of all translation units before hashing them into a single hash value that describes the program's run-time behavior enables TASTING to assess whether a change affects a program with fine granularity. The hash, called semantic fingerprint, is particularly useful when dealing with unit tests. Before the execution of a test, TASTING calculates its semantic fingerprint. If the fingerprint is already known, the result of a test is as well. If not, the test is executed and its result is stored with the fingerprint in a database. TASTING significantly reduces the number of tests executed in a CI scenario, especially for static compile-time variants. The paper was presented at ICSOFT '22 where it received the best student paper award.
Tailoring of Shared Libraries
Shared libraries are generally designed as reusable, general-purpose collections of related functionality which can be accessed by application programs. However, in a strictly defined deployment scenario - like an embedded device - only a small part of the entire functionality might actually be required by the applications present on the device. As it is often impossible to customize shared libraries in a fine-grained manner during the build process, and as we might not have access to their original source code, we developed a lightweight binary tailoring method to detect and remove unneeded code from shared libraries. By combining static and dynamic analysis, we determine which functions are needed in the deployment scenario, delete unused functions from the binary files and shrink the library files by compressing the memory layout on disk. Our tools and the evaluation data for the paper presented at EMSOFT 2019 are available in our GitLab repository.
PaStA: Patch-Stack Analysis
PaStA quantitatively analyses the evolution of patch stacks by mining git repositories and produces data that can serve as input for statistical analysis. It compares different releases of stacks and groups similar patches (patches that lead to similar modifications) into equivalence classes. This allows us to compare those classes against the base project to measure integrability and influence of the patch stack on the base project. PaStA is furthermore able to map mails from mailboxes (e.g., dumps of mailing lists or public inboxes) to commit hashes of repositories. This makes it possible to trace the evolution of patches on mailing lists, like the LKML.
Multiverse
While static variability can be completely resolved at compile time, dynamic variation points come at a cost arising from extra tests and branches in the control flow. Multiverse is an approach to handle dynamic variability efficiently by means of binary patching. It provides an extension to the C programming language that enables the developer to express dynamic variability in performance-critical paths. With specially annotated config variables, multiverse can generate multiple versions of a function and dynamically binary patch the running system to use the version of the current configuration. The goal is to narrow the gap between dynamic and static variability by allowing the developer to easily employ run-time configurability at zero or low cost.
cHash
During the lifetime of a software project, the compiler is invoked thousands if not hundred-thousands of times. However, the actual source base is only gradually changing. In combination, a high number of compilations is redundant and could be avoided. A lower number of compiler invocations will not only speed up the development process since the developer does not have to wait for the compiler, but it also saves resources in terms of precious joules. The cHash compiler plugin detects redundant builds precisely via the mechanism of AST hashing. The result of the AST hash operation is a semantic fingerprint of a single compilation unit. If the fingerprint does not change, the resulting object file will be semantically equivalent. The paper was presented at USENIX '17 where it received the best paper award.
vampyr
This tool is a wrapper for undertaker to do coverage analysis or variability-aware static analysis on source files. For the static analysis compilers such as gcc or clang are employed. Please refer to the USENIX '14 paper for detailed information.
undertaker-checkpatch
This tool reports changes to defects such as newly introduced or fixed defects. Defects can also be correlated to changes in Kconfig and the build system (Make, Kbuild) and vice versa. Additionally, undertaker-checkpatch ships the functionality to further analyze the causes of defects, displaying contradictory Kconfig items, a block's precondition or the defect causing formula. Since version 1.6, undertaker is able to minimize defect formulas (thanks to the PicoMUS-Tool which is part of PicoSAT). This functionality can be used in undertaker-checkpatch to further analyze and understand the cause of defects.
Flipper: Lightweight Kernel Tailoring
Configuring Linux is hard. With over 14,000 options to choose from, making an informed decision about every single one of them takes a very long time. While distributions for standard day-to-day use simply enable as many features (drivers, supported platforms, ...) as possible, this is not a practical solution for embedded systems, where memory is scarce and must not be wasted. To make it easier for an engineer to derive a small starting point to configure the system, we developed Flipper. Flipper provides a lean method to trace which functionality was exerted in the kernel. Using the Tailor tool from the undertaker package, a small, use-case specific configuration for Linux can be generated from the collected data. Flipper is part of undertaker release (v1.6) and can be downloaded here, for detailed usage instructions please read the README file provided in the tailor/flipper subdirectory.
Wundertaker
Wundertaker is a Web GUI visualizing #ifdefs and undertaker's defect reports in Linux code files. The source including installation instructions can be downloaded here. A detailed description of the tool and its implementation can also be found in the Bachelor's thesis of Patrick Plagwitz.
People
Latest News
Tobias Landsberg was invited to give a presentation on “Reducing Deployment Costs for Compile-Time Variants by Static Analysis” as part of the third seminar of the INTER² Series at University of Luxembourg.
In his presentation, he speaks about his research on static variability, or more precisely about the leveraging of similarities and differences in software product lines in order to save costs, time, and energy, which is taking place as part of the CADOS project.The SRA team got two papers accepted for the 2023 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (ATC '23). Lars Wrenger is going to present our paper LLFree: Scalable and Optionally-Persistent Page-Frame Allocation, which is an extension of his award-winning master's thesis and an important building block for the ParPerOS project. Dominik Töllner is going to present the paper MELF: Multivariant Executables for a Heterogeneous World, which is a great success for the ATLAS and CADOS projects. Congrats to Lars and Dominik, this is a really great achievement for first-year doctoral researchers!
Publications
-
SPLC
Conference
B
Should I Bother? Fast Patch Filtering for Statically-Configured Software Variants -
Proceedings of the 28th Software Product Line Conference (SPLC '24)ACM Press2024Accepted.
[BibTex]
-
USENIX
Conference
A
MELF: Multivariant Executables for a Heterogeneous World -
2023 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX '23)USENIX Association2023.
PDF Details [BibTex]
-
LCTES
Conference
B
Thread-Level Attack-Surface Reduction -
Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGPLAN/SIGBED International Conference on Languages, Compilers, and Tools for Embedded SystemsACM Press2023.
PDF Details Slides Video 10.1145/3589610.3596281 [BibTex]
-
Thesis
Automated Tailoring of System Software Stacks -
PHD thesisLeibniz Universität Hannover2023.
PDF 10.15488/15610 [BibTex]
-
ICSOFT
Conference
B
Best Student Paper
TASTING: Reuse Test-case Execution by Global AST Hashing -
Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Software Technologies - ICSOFTSciTePress2022Best Student Paper.
PDF 10.5220/0011139200003266 [BibTex]
-
PLOS
Workshop
C
CppSig: Extracting Type Information for C-Preprocessor Macro Expansions -
Proceedings of the 11th SOSP Workshop on Programming Languages and Operating Systems (PLOS '21)ACM2021.
PDF Slides Video Teaser Video Raw Data 10.1145/3477113.3487268 [BibTex]
-
Thesis
OSS Architecture for Mixed-Criticality Systems: A Dual View from a Software and System Engineering Perspective -
PHD thesisLeibniz Universität Hannover2021.
PDF 10.15488/11722 [BibTex]
-
OSDI
Conference
A*
From Global to Local Quiescence: Wait-Free Code Patching of Multi-Threaded Processes -
14th Symposium on Operating System Design and Implementation (OSDI '20)2020.
PDF Details Video [BibTex]
-
CCSW
Workshop
The Sound of Silence: Mining Security Vulnerabilities from Secret Integration Channels in Open-Source Projects -
Proceedings of the 12th Cloud Computing Security Workshop (CCSW '20)ACM2020.
PDF Video 10.1145/3411495.3421360 [BibTex]
-
EMSOFT
Journal
A
Honey, I Shrunk the ELFs: Lightweight Binary Tailoring of Shared Libraries -
ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems18.5sACM Press2019.
PDF Raw Data 10.1145/3358222 [BibTex]
-
ICSE
Conference
A*
The List is the Process: Reliable Pre-Integration Tracking of Commits on Mailing Lists -
Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE '19)2019.
PDF Raw Data 10.1109/ICSE.2019.00088 [BibTex]
-
EuroSys
Conference
A
Multiverse: Compiler-Assisted Management of Dynamic Variability in Low-Level System Software -
Fourteenth EuroSys Conference 2019 (EuroSys '19)ACM Press2019.
PDF Slides 10.1145/3302424.3303959 [BibTex]
-
PLOS
Workshop
B
Wait-Free Code Patching of Multi-Threaded Processes -
Proceedings of the 10th SOSP Workshop on Programming Languages and Operating Systems (PLOS '19)ACM2019.
PDF 10.1145/3365137.3365404 [BibTex]
-
USENIX
Conference
A
Best Paper Award
cHash: Detection of Redundant Compilations via AST Hashing -
Proceedings of the 2017 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX '17)USENIX Association2017Best Paper Award.
PDF Details Slides Raw Data [BibTex]
-
VAMOS
Workshop
Analyzing the Impact of Feature Changes in Linux -
Proceedings of the Tenth International Workshop on Variability Modelling of Software-intensive Systems2016.
PDF 10.1145/2866614.2866618 [BibTex]
-
VAMOS
Workshop
Feature Models in Linux - From Symbols to Semantic -
Proceedings of the Tenth International Workshop on Variability Modelling of Software-intensive Systems2016.
PDF 10.1145/2866614.2866624 [BibTex]
-
OpenSym
Conference
Observing Custom Software Modifications: A Quantitative Approach of Tracking the Evolution of Patch Stacks -
Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Open Collaboration (OpenSym '16)2016.
PDF 10.1145/2957792.2957810 [BibTex]
-
GPCE
Conference
B
Towards Scalable Configuration Testing in Variable Software -
Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Generative Programming: Concepts and Experiences (GPCE '16)2016.
PDF 10.1145/2993236.2993252 [BibTex]
-
OSR
Journal
The dataref versuchung -
ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review: Special Issue on Repeatability and Sharing of Experimental ArtifactsACM Press2015.
PDF 10.1145/2723872.2723880 [BibTex]
-
GPCE
Conference
B
Automatic Feature Selection in Large-Scale System-Software Product Lines -
Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Generative Programming and Component Engineering (GPCE '14)ACM Press2014.
PDF 10.1145/2658761.2658767 [BibTex]
-
USENIX
Conference
A
Static Analysis of Variability in System Software: The 90,000 #ifdefs Issue -
Proceedings of the 2014 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX '14)USENIX Association2014.
PDF Raw Data [BibTex]
Theses
Currently Running
Implementing Content-Based Regression Test Selection Using the LLVM Intermediate Representation
- Typ
- Masterarbeit
- Status
- laufend
- Supervisors
- Tobias Landsberg
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Tino Lorenz
Integration and Optimization of a Variability-Aware LLVM-Based Toolchain for Highly Configurable Software
- Typ
- Bachelorarbeit
- Status
- laufend
- Supervisors
- Tobias Landsberg
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Johannes Grunenberg
Finished Theses
Multiverse: Compiler-Assisted Dynamic Variability Management in the Linux Kernel
- Typ
- Masterarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Christian Dietrich
Andreas Ziegler
Wolfgang Schröder-Preikschat
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Florian Rommel (abgegeben: 02. Nov 2017)
Avoidance of Redundant Recompilations by Propagation of Semantic Fingerprints
- Typ
- Bachelorarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Christian Dietrich
Daniel Lohmann
Integration of AST Hashing into the GCC compiler
- Typ
- Bachelorarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Christian Dietrich
Daniel Lohmann
Measurement-Directed Application of Compiler-Assisted Dynamic Variability Management in the Linux Kernel
- Typ
- Masterarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Florian Rommel
Christian Dietrich
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Michael Rodin (abgegeben: 01. Oct 2018)
Bintail: Binary Level Tailoring of ELF Executables via Feature Selection and Variant Elimination
- Typ
- Masterarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Florian Rommel
Christian Dietrich
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Felix Herrmann (abgegeben: 01. Nov 2018)
Run-Time Binary Patching for Systems with Dynamically Loadable Modules
- Typ
- Bachelorarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Florian Rommel
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Dominik Töllner (abgegeben: 01. Sep 2019)
Extending the Linux Kernel for Wait-Free Live Patching of Multi-Threaded Processes
- Typ
- Masterarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Florian Rommel
Christian Dietrich
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Lennart Glauer (abgegeben: 20. Nov 2019)
How to trust the Snake: Extending the Chain of Trust to Interpreted Languages on Highly Embedded Systems
- Typ
- Bachelorarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Stefan Naumann
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Lars Wrenger
Investigating Non-Disruptive Checkpoints via Address-Space Clones in Linux-Based Non-Volatile Memory Systems
- Typ
- Masterarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Florian Rommel
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Sergej Perschin
Implementierung und Evaluation eines FUSE-Dateisystems für Linux zur Integration erweiterter Änderungsdetektionsverfahren in Buildsystemen
- Typ
- Bachelorarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Tobias Landsberg
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Malte Müller (abgegeben: 08. Aug 2020)
Entwurf und Implementierung einer leichtgewichtigen Linux-Programmbibliothek für persistent-adressierte, nicht-flüchtige Speicherbereich
- Typ
- Bachelorarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Stefan Naumann
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Niklas Hoh
Erweiterung des Linux-Kerns um mehrstufige Seitenumlagerung für Systeme mit nichtflüchtigem Speicher (NVM)
- Typ
- Masterarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Stefan Naumann
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Christian Müller
Vermeidung von Seitenfehlern zum Programmstart durch einen persistent-prädiktiven Seitenzwischenspeicher im Linux Kern
- Typ
- Masterarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Stefan Naumann
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Simon Burandt
Efficient Change Impact Quantification by Global AST Hashing
- Typ
- Masterarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Tobias Landsberg
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Maximilian Werner (abgegeben: 05. Nov 2021)
Multiverse: Extending LLVM by Compiler-Assisted Dynamic Variability
- Typ
- Bachelorarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Tobias Landsberg
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Nils Fuhler (abgegeben: 19. Sep 2022)
Multiverse: Extending LLVM by Compiler-Assisted Dynamic Variability for Structs
- Typ
- Forschungsprojekt
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Tobias Landsberg
Florian Rommel
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Nishal Kulkarni
DynMELF: Extending the LLVM Linker to Support Dynamic Library Switching in MELFs
- Typ
- Bachelorarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Dominik Töllner
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Jens Köneke (abgegeben: 08. Oct 2023)
Extending GNU Make With Custom Fingerprints to Reduce Redundant Recompilation
- Typ
- Bachelorarbeit
- Status
- abgeschlossen
- Supervisors
- Tobias Landsberg
Daniel Lohmann - Bearbeiter
- Sergej Reich